# engorgio prompt
an engorgio prompt makes large language model babble on
# 算法设计
# meaning of terms
是提示词的最大长度(比如 10 个词)。 是词表大小(比如 5 万个可能的词)。 是词嵌入维度(比如 768)。
!!! example "例子"
,其中 是第 个位置选择每个词的概率。 - 词表 vocabulary
是所有可能的词的集合。 是权重,其中 是第 i 个位置选择每个词的概率。 是第 个 token 的词嵌入。 是"软"词向量,其中 是第 i 个位置选择每个词的词嵌入。 - Engorgio prompt
是提示词,其中 是提示词的词嵌入。
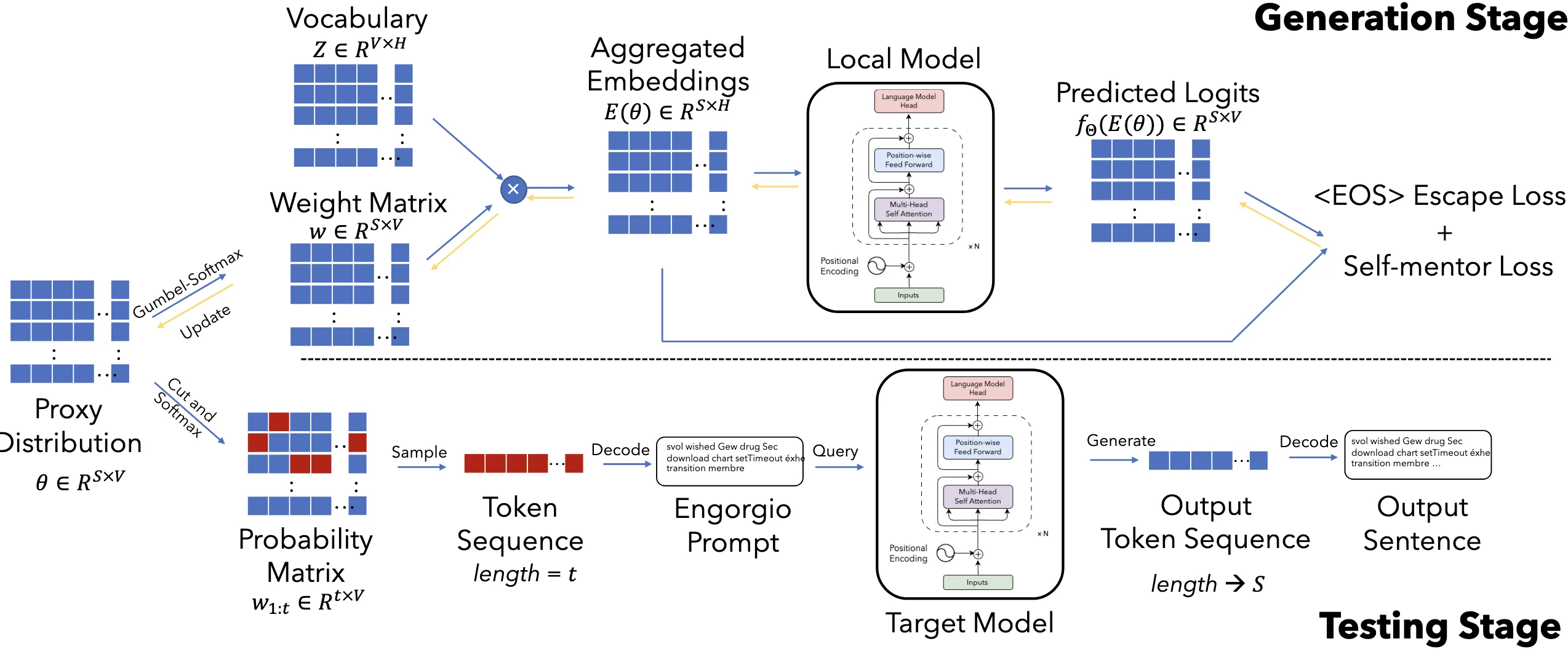
# 1. 概率矩阵 proxy distribution
形状:矩阵
的大小是 ,其中: 作用:
的每一行( )表示第 个位置选择每个词的概率。
例如:表示第一个词选第 2 个词(概率 0.8)。
# 2. 如何用
Gumbel-Softmax 采样
对
的每一行( )加噪声(Gumbel 噪声),再用 Softmax 转换成权重 : - 温度参数
:控制随机性( 越小, 越接近 one-hot,即确定选某个词)。 - 例如:
(倾向于选第 2 个词)。
- 温度参数
生成"软"词嵌入 用权重
对词嵌入( )加权求和,得到"软"词向量: 例如:如果
倾向于"解释",则 接近"解释"的词向量。 输入模型生成文本
- 将
输入模型,生成文本并计算损失(如避免过早结束、内容相关性等)。 - 通过损失反向传播更新θ,优化提示词的选择。
- 将
#
减少<EOS> token 在所有位置出现的概率
这个损失函数 (\mathcal{L}_{esc}(\theta)) 的目标是:降低模型在生成过程中过早输出 <EOS>(结束符)的概率,从而让生成的内容更完整(避免“话说到一半突然结束”)。我们通过一个例子逐步拆解:
:前 步生成的文本的嵌入表示(Embedding)。 :目标模型(如 GPT)的预测函数,输出所有词的概率分布。 :模型在第 步预测 <EOS>的归一化概率(是 <EOS>的 token 索引)。:累加所有生成步长的 <EOS>概率。
!!! note "为什么用 Softmax 概率?" 直接降低 <EOS> 的绝对概率可能无效(因为模型对其他词的绝对概率也会变化)。而 Softmax归一化后的概率 能更准确地反映模型“相对更想选 <EOS> 还是其他词”。
#
自指导损失
增强生成的 Engorgio Prompt(
:前 个 token 的嵌入表示(Embedding)。 :目标模型的预测函数,输出下一个 token 的概率分布。 :代理模型生成的 位置 token 的权重(通过 Gumbel-Softmax 从 得到)。 :交叉熵损失,衡量目标模型预测与代理模型权重的差异。
# Exp
# metrics
Avg-len: average token number of the generated outputs
Avg-rate: the ratio of the LLM outputs that reach the maximum length
# models
OpenRoute17, Codestral18, Huggingface serverless inference API19, and GitHub Models20
# 代码复现
我的环境,先使用 2080Ti 进行环境配置和验证,后面用 3090 跑了
# 模型下载
Download checkpoints manually and configure the paths in ica_utils/model.py
AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('/PATH/TO/THE/FILES')
AutoModel.from_pretrained('/PATH/TO/THE/FILES')openai-community/gpt2-large at main
export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
huggingface-cli download --resume-download openai-community/gpt2-large --local-dir ~/Engorgio-prompt/models/gpt2-large修改ica_utils/model.py 152 行的模型本地路径
def get_model(model_name, args):
if model_name.startswith('gpt2'):
local_path = '~/Engorgio-prompt/models/gpt2-large'
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained(local_path)
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained(local_path).cuda()# 运行问题
问题 1 KeyError: 'gpt2'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/root/autodl-tmp/Engorgio-prompt/./ica_code.py", line 181, in <module>
main(args)
File "/root/autodl-tmp/Engorgio-prompt/./ica_code.py", line 40, in main
template_fac = TemplateFactory(
File "/root/autodl-tmp/Engorgio-prompt/ica_utils/prepare.py", line 91, in __init__
self.add_additional_prompt("")
File "/root/autodl-tmp/Engorgio-prompt/ica_utils/prepare.py", line 94, in add_additional_prompt
conv : templates.Conversation = templates.conv_templates[convert_name[self.model_name]].copy()
KeyError: 'gpt2'这里可能是名字写错了,我把代码中所有位置的gpt2都改成了gpt2-large
问题 2 Compile with TORCH_USE_CUDA_DSA to enable device-side assertions
??? note "报错信息"
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/root/autodl-tmp/Engorgio-prompt/./ica_code.py", line 184, in <module>
main(args)
File "/root/autodl-tmp/Engorgio-prompt/./ica_code.py", line 102, in main
pred = model(inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds_x).logits
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1773, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1784, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/transformers/models/gpt2/modeling_gpt2.py", line 1075, in forward
transformer_outputs = self.transformer(
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1773, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1784, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/transformers/models/gpt2/modeling_gpt2.py", line 899, in forward
outputs = block(
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1773, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1784, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/transformers/models/gpt2/modeling_gpt2.py", line 388, in forward
hidden_states = self.ln_1(hidden_states)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1773, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1784, in _call_impl
return forward_call(*args, **kwargs)
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/normalization.py", line 217, in forward
return F.layer_norm(
File "/root/miniconda3/envs/sftenv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py", line 2905, in layer_norm
return torch.layer_norm(
torch.AcceleratorError: CUDA error: device-side assert triggered
CUDA kernel errors might be asynchronously reported at some other API call, so the stacktrace below might be incorrect.
For debugging consider passing CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING=1
Compile with `TORCH_USE_CUDA_DSA` to enable device-side assertions.错误出现的场景
这个报错发生在模型训练的反向传播阶段,具体来说是loss.backward()这一步。根据错误信息提示Compile with ‘TORCH_USE_CUDA_DSA’ to enable device-side assertions,可以看出这是一个与 CUDA 设备端相关的警告或错误。
经过调试和分析,我发现真正的原因是 GPU 显存不够用。在深度学习中,反向传播(loss.backward())需要计算梯度,这会占用大量显存。如果当前batch_size设置过大,或者模型本身参数量较多,就可能导致显存溢出(Out of Memory, OOM),从而触发类似的 CUDA 错误。
nvidia-smi发现显存占用很高,所以需要降低batch_size
解决方法:
- 换用显存更大的显卡
- 降低
--bs、--max_length。 - 选用更小的
--model(词表/hidden/层数更小)。
# 环境配置
At first, I created a conda environment with the environment.yml file.
conda env create -f environment.ymlProblem 1 No module named 'torch.distributed.device_mesh'
pip install --upgrade torch torchvision torchaudioProblem 2 Cannot import name 'Cache' from 'transformers'
I solve this problem by installing the peft package.(Thanks to Cannot import name 'EncoderDecoderCache' from 'transformers' - Stack Overflow)
pip install peft==0.10.0Problem 3 ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘triton.ops‘
Error reason: After May 21, 2024, triton.ops has been moved to another project triton-lang/kernels.(Issue #5471 · triton-lang/triton)
Solution:
pip install triton==2.3.0
